- Set the environment:
$ORACLE_HOME to the OC4J home
$JAVA_HOME your JDK home
- Start the OC4J with the
following property set
$JAVA_HOME/bin/java -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -jar oc4j.jar
The -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote system property creates an RMI connector to the MBeanServer, we will use this RMI connector from the console iself.
- Start the JConsole, with the
following command, adding the OC4J administration class to the
classpath.
$JAVA_HOME/bin/jconsole -J-Djava.class.path=$JAVA_HOME/lib/jconsole.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar;$ORACLE_HOME/lib/adminclient.jar
- The console will
automatically ask you to connect to the OC4J process and you can start
to monitor and administer your OC4J instance
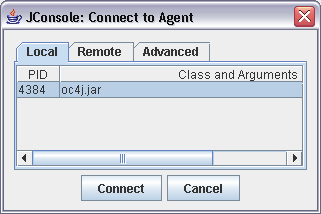
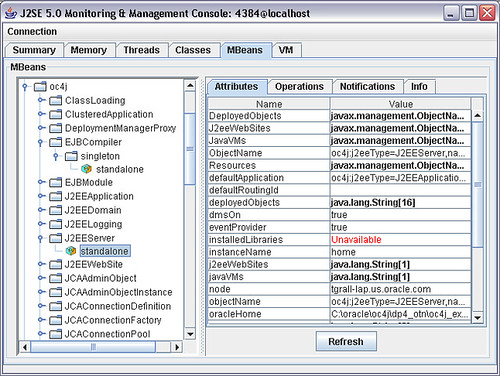
Connection to the OC4J MBean Server
Friday, September 16, 2005
Administer and Monitor OC4J using JConsole
OC4J 10g
(10.1.3) is a J2EE 1.4 containers, so as part of the specifications, it
supports JMX for management and deployment. One of the benefits of JMX
is the fact that finally Java applications, and in our case the J2EE
containers, have a standard based interface to be administered. OC4J
exposes using its MBean Server system and application lever management
beans (MBeans) that you can monitor and control from the Oracle
Application Server Control (ASC) that is pre-deployed; but you can use
any JMX client application. Sun has included as part of Java 5 JMX but
also provides a standard JMX client called JConsole. This post is
simply explaining how you can use the Sun's JConsole with OC4J.
No comments:
Post a Comment